
Output Successfully compiled and executedīase 4: Since ArrayList can’t be created for primitive data types, members of ArrayList are always references to objects at different memory locations (See this for details). ArrayList is a part of the collection framework and is present in java.util package. It can be shrunk or expanded based on size. Note: ArrayList in Java (equivalent to vector in C++) having dynamic size. Here Type is the type of elements in ArrayList to be created Syntax: Declaring an Arraylist Arraylist al = new ArrayList Now let us dwell on the next concept of ArrayList that is as follows It is very important statement and is left unveiliable when it comes to deep understanding of memory storage in arrays. Note: arr(0) returns the first element of the array so it does mean that if we try to print out arr(0) then we will get Element1. which is containing continuous 100 block associated in it
This does means we are declaring a memory block named 'arr' It is preferable if we have very limited array elements
#Array vs arraylist vs linkedlist java how to#

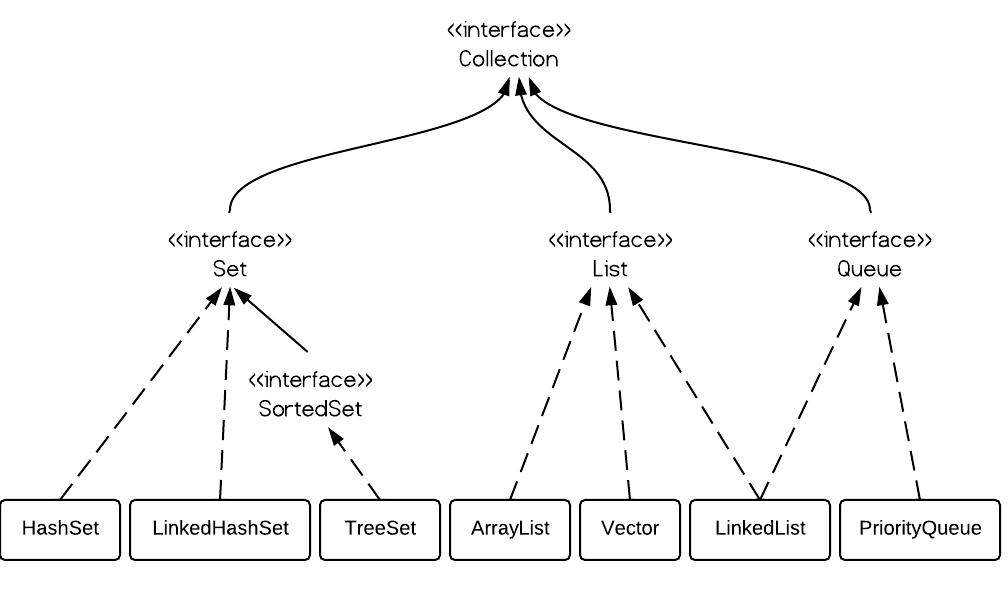
This class implements both the List interface and the Deque interface. The list is traversed and the reference link is changed. Manipulating LinkedList takes less time compared to ArrayList because, in a doubly-linked list, there is no concept of shifting the memory bits. Whenever we remove an element, internally, the array is traversed and the memory bits are shifted. Manipulating ArrayList takes more time due to the internal implementation.

Similar to the ArrayList, this class also supports the storage of all types of objects. This class uses a doubly linked list to store the elements in it. With the introduction of generics, this class supports the storage of all types of objects. Now after having an adequate understanding of both of them let us do discuss the differences between ArrayList and LinkedList in Java ArrayList LinkedList This class uses a dynamic array to store the elements in it.

Using _ (underscore) as variable name in Java.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
